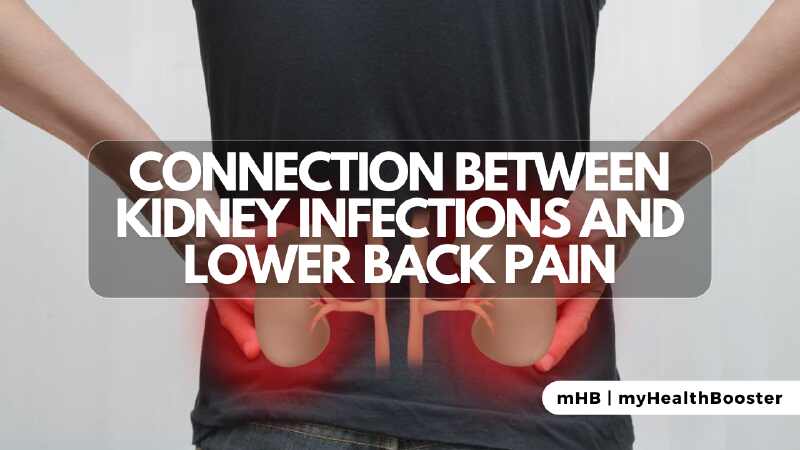
Lower back pain is a common ailment with various potential causes, ranging from spinal trauma to lifestyle factors. However, when accompanied by symptoms like frequent urination, blood in the urine, fever, or chills, it could signify a kidney infection, medically known as Pyelonephritis. This article delves into the relationship between kidney infections and back pain, highlighting symptoms, types, causes, when to seek medical attention, and the diagnostic and treatment processes.
Kidney Function Overview
Under normal conditions, the kidneys play a vital role in filtering water and waste from the blood, producing urine, and maintaining overall bodily functions. They also balance electrolytes, regulate red blood cells, and control blood pressure.
Signs and Symptoms of Kidney Infection
Common indicators of kidney infection include lower back or groin pain, frequent or urgent urination, bloody or cloudy urine, nausea, vomiting, fever, and chills. Symptoms may vary by age, making it essential to recognize cognitive issues, especially in older adults, such as difficulty speaking and confused thinking.
Types and Causes of Kidney Infection
Kidney infections can be caused by viruses or bacteria, often originating from the bowel and migrating to the urinary tract. The urinary tract typically prevents bacterial entry, but factors like urinary tract infections, spinal cord injuries, pregnancy, or other medical conditions can increase susceptibility.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While isolated lower back pain may resolve on its own, persistent or worsening pain, coupled with symptoms like fever or chills, should prompt a doctor visit. Kidney infections can lead to severe complications, including sepsis, necessitating immediate medical attention.
Diagnosing Kidney Infection
Given that lower back pain can have various origins, a precise diagnosis is crucial. Doctors may conduct a physical examination, review medical history, and perform tests such as blood and urine cultures, ultrasounds, prostate exams, or digital imaging to determine the cause accurately.
Treatments for Kidney Infection
Antibiotics are the primary treatment for kidney infections, administered orally or intravenously depending on the severity. The choice of antibiotic may involve analyzing blood and urine samples to ensure effectiveness. In cases of urinary tract blockages, additional procedures or surgery may be necessary to address the underlying issue.
In Brief
Kidney infections should not be taken lightly, as they can lead to severe health complications. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding when to seek medical attention, and following prescribed treatments are essential for managing kidney infections effectively. Prompt intervention and adherence to medical advice contribute significantly to successful outcomes in treating kidney-related back pain. If in doubt, consult a healthcare professional to ensure proper diagnosis and timely intervention.
References
- Johns Hopkins: “Lower Back Pain: What Could It Be?”
- Mount Sinai: “Flank pain.”
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: “Definition & Facts of Kidney Infection (Pyelonephritis).”
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: “What are the symptoms of kidney infections?”
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: “Treatment for Kidney Infection (Pyelonephritis)”
- National Kidney Foundation: “Top 10 Things to Know About Urinary Tract Infections.”
- Rush University for Health: “Kidney Infection.”
- Urology Care Foundation: “Kidney (Renal) Infection – Pyelonephritis.”
- U.S. National Library of Medicine: Urinary tract infection – adults.”